Electric vehicles (EVs) are on the rise, and for good reason: they reduce emissions, lower fuel costs, and represent the future of transportation. But their popularity comes with a wave of viral headlines about car battery fires, raising questions like: Why do EV batteries catch fire? Can car batteries explode? And ultimately — are electric cars a fire hazard?
While EV battery fires are rare compared to the number of vehicles on the road, they can be more dangerous and difficult to manage than traditional car fires. The reasons lie in the chemistry of lithium-ion batteries and the unique risks that come with storing massive amounts of energy in a compact, flammable package.
In this article, we’ll break down the science behind EV batteries, why electric cars sometimes catch fire, the conditions that increase those risks, and what can be done to prevent and manage these incidents — especially in commercial and industrial settings where multiple vehicles or battery packs may be stored together.
The Science Behind EV Batteries
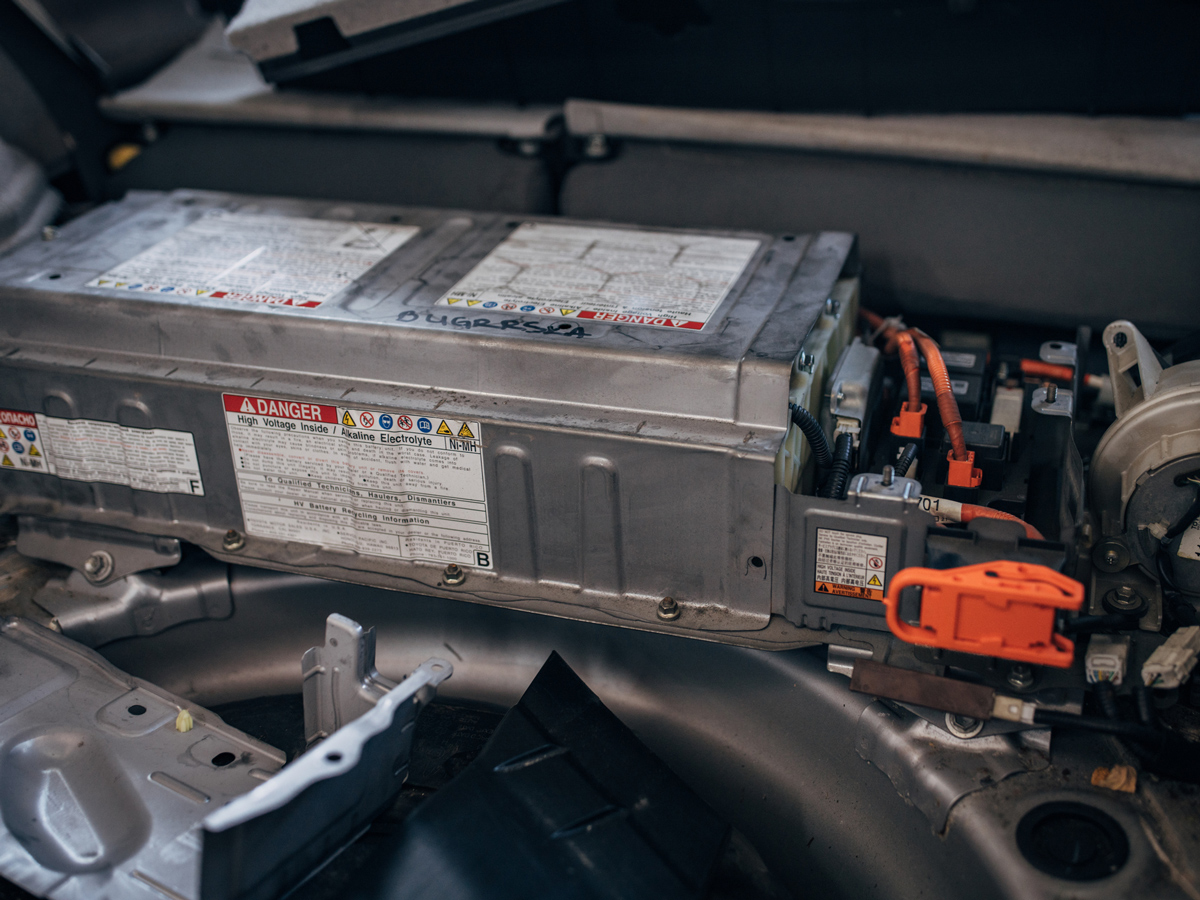
At the heart of nearly every electric vehicle is a lithium-ion battery, the same general type found in laptops, smartphones, and power tools — only much larger. These batteries consist of a cathode, anode, separator, and electrolyte. During charging and discharging, lithium ions move between the electrodes through the electrolyte, storing and releasing energy.
What makes these batteries powerful also makes them volatile. They have:
- High Energy Density: EV batteries pack enormous amounts of energy into a relatively small space.
- Flammable Electrolyte: The liquid electrolyte inside is often highly flammable.
- Thermal Runaway Risk: If one cell overheats, it can trigger a chain reaction in neighboring cells, causing temperatures to rise uncontrollably.
Compared to traditional lead-acid car batteries, lithium-ion batteries are far more efficient — but also more prone to thermal runaway, which is the primary driver of EV fires. Once thermal runaway begins, temperatures can exceed 1,000°F, igniting the electrolyte and releasing toxic gases.
Common Causes of EV Battery Fires
So, why do electric cars catch fire in the first place? While rare, when EV battery fires do occur, they often stem from one of the following causes:
1. Internal Failures
A defect inside a cell, like a short circuit or overheating, can start a localized failure that cascades through the entire pack.
2. Manufacturing or Design Flaws
Even small imperfections — like microscopic metal particles left during production — can compromise the battery’s integrity. Automakers have recalled thousands of vehicles over such issues.
3. Physical Damage
Accidents or improper handling can puncture the battery pack, damaging cells and exposing them to air or moisture. This can cause a short circuit or direct ignition.
4. Charging and Electrical Issues
Overcharging, faulty charging equipment, or poor electrical connections can trigger overheating. Rapid charging stations, while generally safe, put additional stress on battery systems if not properly managed.
Each of these factors increases the chance of a car battery fire, which in turn leads people to ask: why do car batteries explode? In the case of lithium-ion packs, the “explosion” is usually a violent release of gases during thermal runaway, which may look explosive even if it’s technically rapid combustion.
Where and When Do EV Battery Fires Typically Occur?
EV battery fires aren’t random; they tend to happen in specific circumstances:
- During Charging: Batteries are stressed, and any malfunction can escalate quickly.
- After Collisions: Damaged cells may smolder for hours before igniting.
- In Storage and Transport: Large numbers of batteries or vehicles kept together increase the risk of a single fire spreading rapidly.
- At Recycling Facilities: Spent or damaged batteries that are improperly stored can ignite, creating large industrial fires.
Because of these scenarios, both first responders and facility managers must remain vigilant. A single car battery fire can be difficult enough to extinguish — but in a warehouse full of EVs or battery packs, the stakes are much higher.
Risk Factors That Increase the Chances of Electric Car Fires
Not every EV is equally at risk. Several conditions can raise the likelihood of a fire:
- Environmental Stress: Heat waves, extreme humidity, and flooding all put stress on lithium-ion cells. Exposure to salt water, in particular, can trigger dangerous reactions.
- Battery Age: Over time, batteries degrade, making them more vulnerable to short circuits or instability.
- Improper Disposal: Throwing EV batteries into general waste or recycling streams has led to catastrophic fires at waste facilities.
- High-Stress Commercial Use: Delivery fleets, transit buses, and construction equipment cycle through charges more aggressively, increasing wear and the chances of overheating.
These risks underscore the reality: while not all electric cars are fire hazards, under certain conditions they pose unique fire safety challenges compared to traditional gas-powered vehicles.
Fire Suppression Challenges for EV Batteries
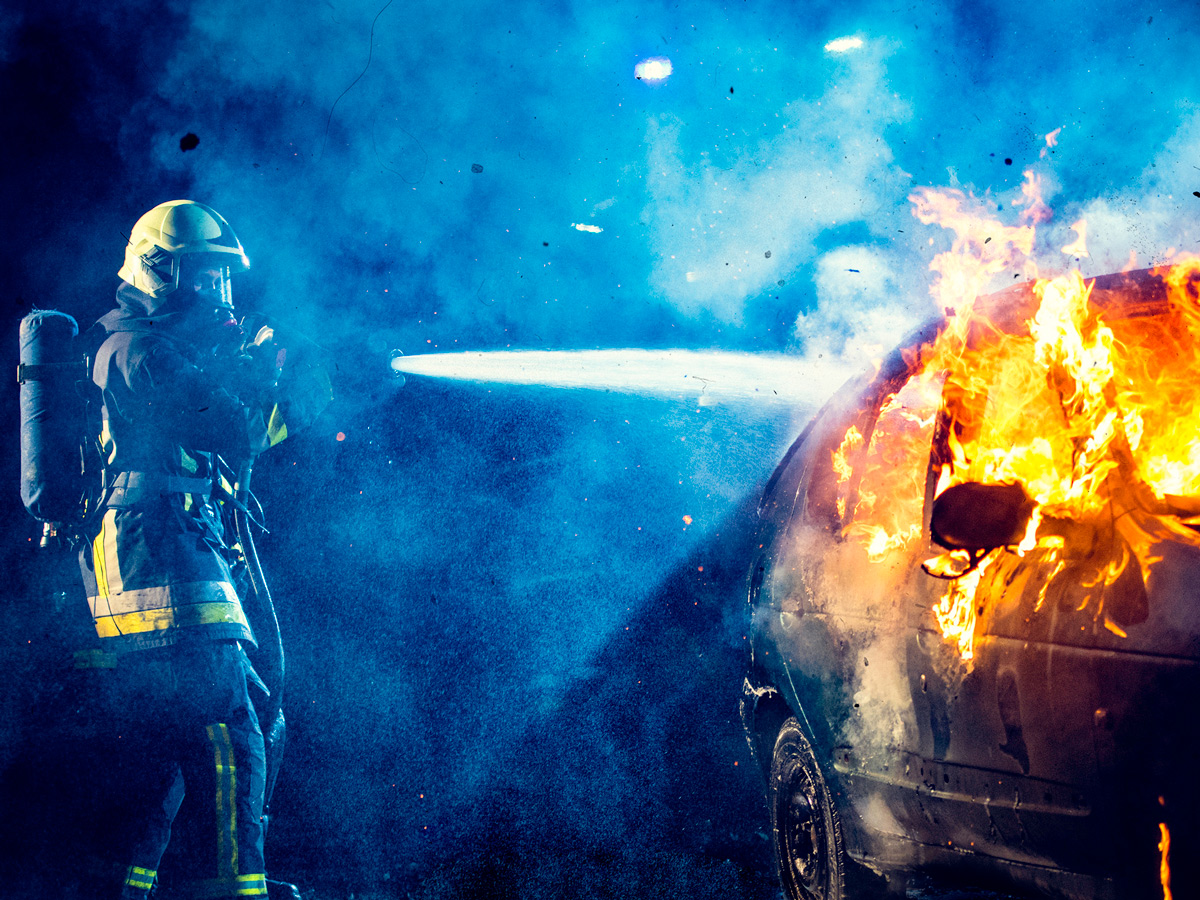
If you’re wondering, can car batteries explode and what happens next — here’s the difficult truth: traditional fire suppression methods often don’t work.
- Water Is Often Ineffective: EV battery packs can reignite hours or even days after appearing to be extinguished. Firefighters sometimes need to submerge entire vehicles in water tanks to prevent reignition.
- Fire Extinguishers Have Limits: Standard extinguishers aren’t designed for the temperatures or chemicals involved in lithium-ion fires.
- Reignition Risk: Even after cooling, damaged cells may self-heat and flare back up.
For facilities that store or process EVs or lithium-ion batteries, this presents a massive challenge. A single incident can escalate into a multi-day industrial fire, overwhelming local fire departments.
Preventing and Managing EV Battery Fires
So what can be done? The best strategy combines prevention, rapid detection, and specialized suppression systems.
Preventive Measures
- Thermal management systems in vehicles regulate heat and prevent overheating.
- Smart charging reduces stress by avoiding overcharging and monitoring for faults.
- Proper handling and storage ensure damaged or aging batteries are isolated.
Emergency Response
- Containment zones can stop a single fire from spreading.
- Trained staff familiar with EV fire risks respond faster and more effectively.
- Specialized equipment like EV fire blankets and lithium-ion suppression systems provide a critical advantage.
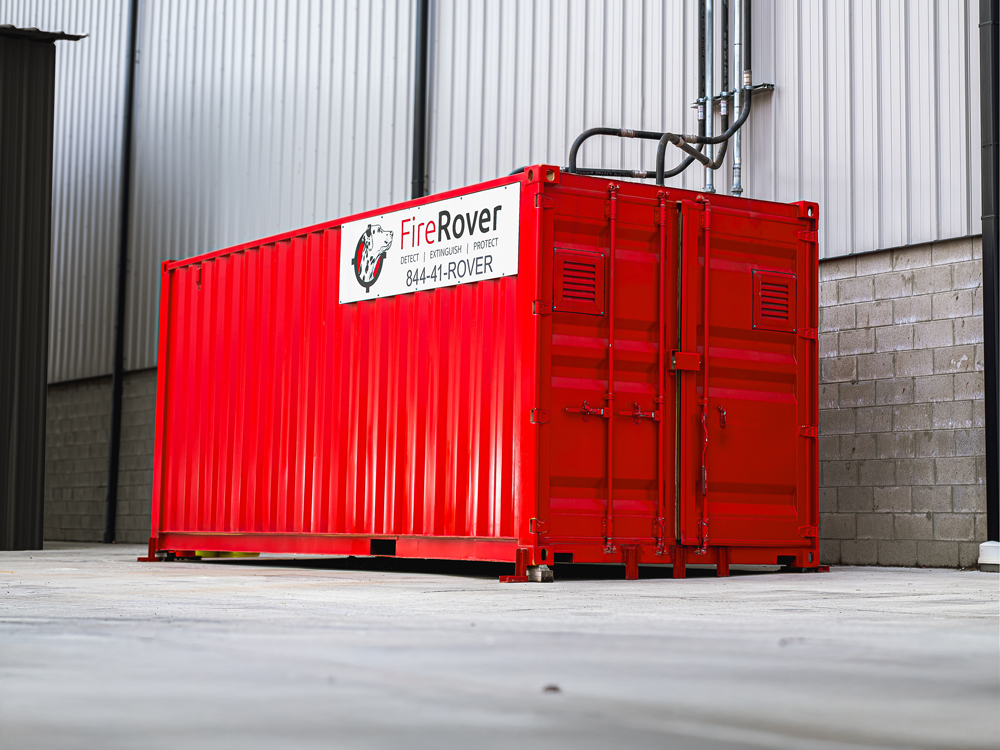
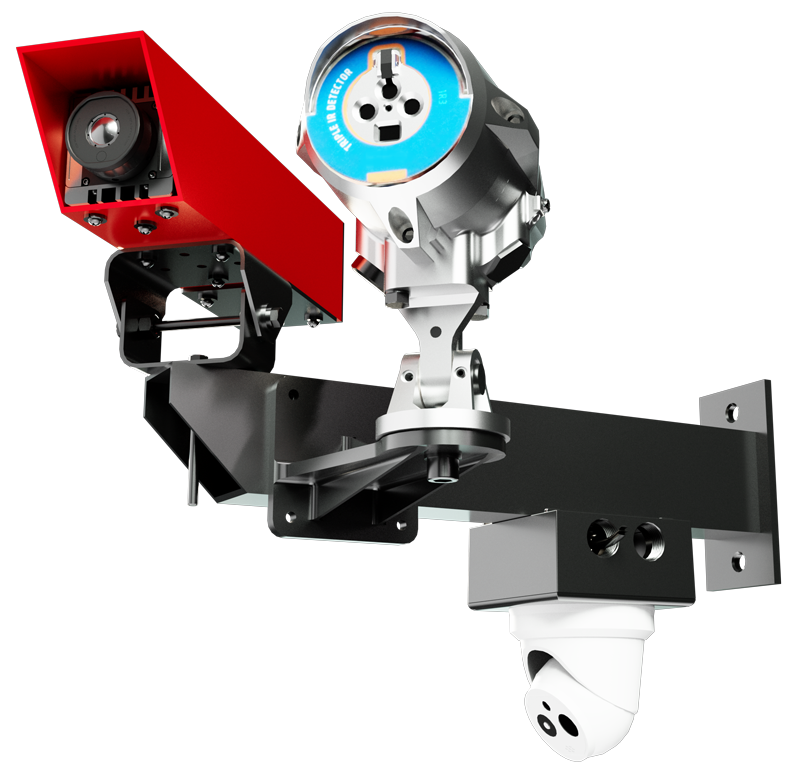
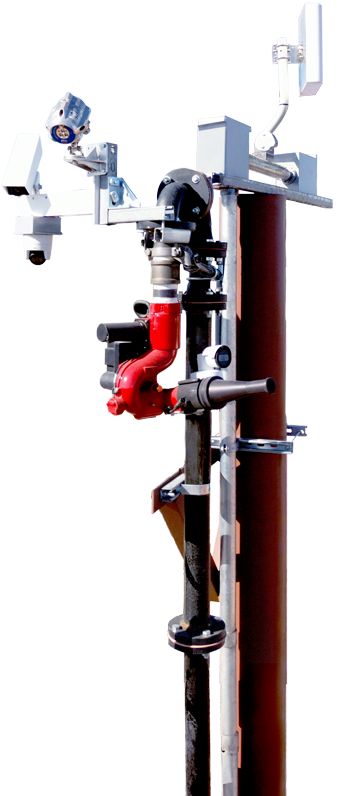
How Fire Rover Can Help
At Fire Rover, we specialize in early fire detection and targeted suppression for high-risk environments. Our systems are specifically designed to monitor facilities 24/7, identify the earliest signs of thermal events, and intervene before a small spark becomes a catastrophic fire. For businesses handling EV batteries, recycling centers, and industrial sites, this level of protection can mean the difference between a minor incident and a total loss.
Protect Your Operations Against EV Battery Fire Risks
As EV adoption grows, so do the challenges of managing their fire risks. While the question “do electric cars catch fire?” has a reassuring answer — not often — the consequences when they do can be severe. Understanding why EV batteries catch fire and investing in prevention and suppression systems is essential for safety, compliance, and peace of mind.
If your facility stores, charges, or recycles EVs and lithium-ion batteries, now is the time to act. Fire Rover can help you build a safer, smarter fire prevention strategy tailored to your needs.
Contact our team today to learn how we can protect your people, assets, and operations.